
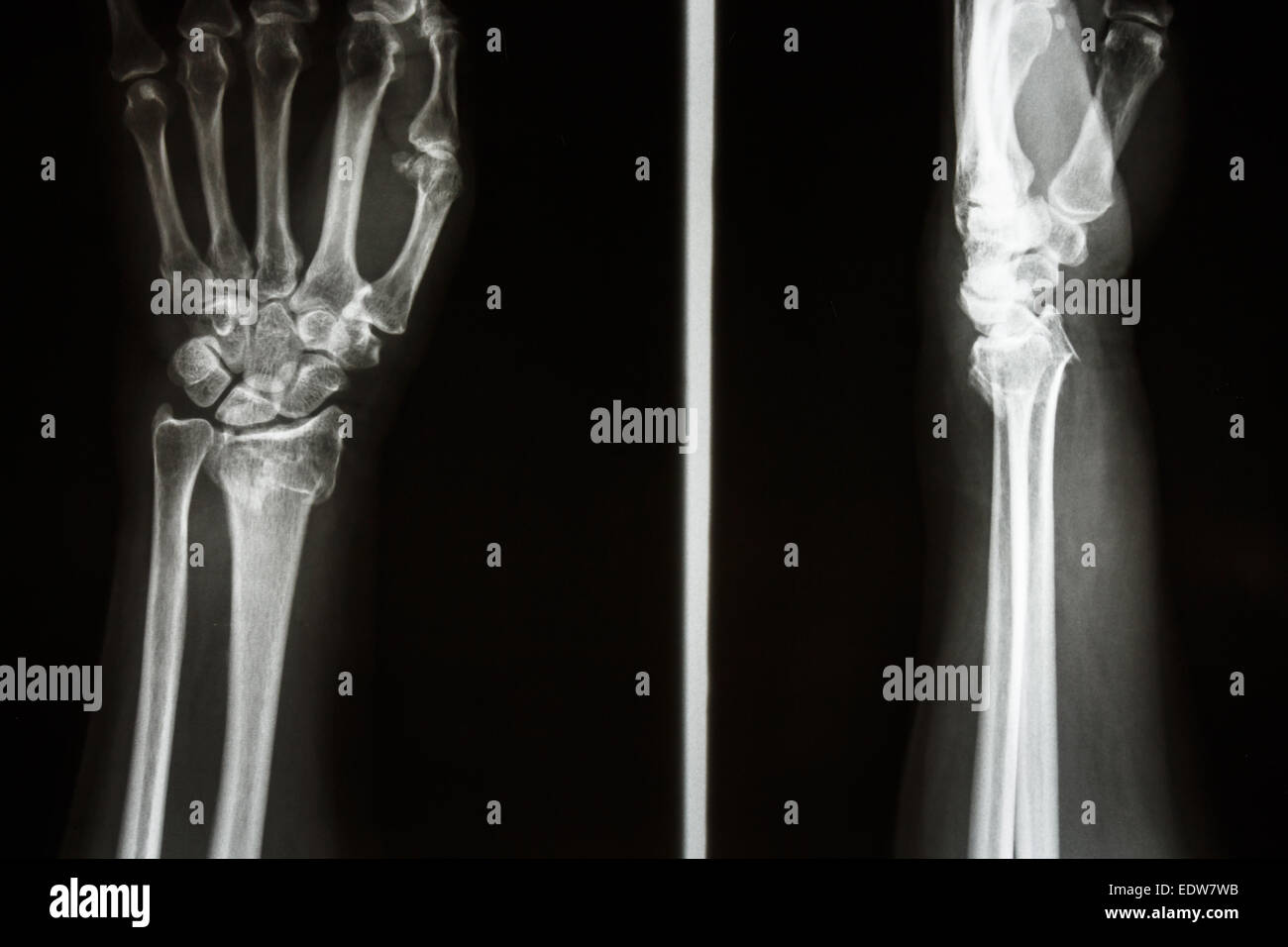
Even then a fracture may not be apparent. If a minimally displaced fracture was present initially, healing will now be apparent. Therefore, people with tenderness over the scaphoid (those who exhibit pain to pressure in the anatomic snuff box ) are often splinted in a thumb spica for 7–10 days at which point a second set of X-rays is taken. In 1/4 of cases, the clinical examination suggests a fracture, but the X-ray does not show it, even though there is indeed a fracture. However, not all fractures are apparent initially. Scaphoid fractures are often diagnosed using plain radiographs and multiple views are obtained as standard. Diagnosis Fracture of the tubercle of the scaphoid bone of the wrist 10%-20% of fractures are at the proximal pole, 60%-80% are at the waist (middle), and the remainder occur at the distal pole. Using the Herbert classification system, there are three main types of scaphoid fractures. Mechanism Scaphoid fractures occur in three locations: (A) Distal tubercle, (B) waist, and (C) proximal pole.įractures of scaphoid can occur either with direct axial compression or with hyperextension of the wrist, such as a fall on the palm on an outstretched hand. Should these treatments not work, surgery may be required. If these treatments do not help the symptoms of arthritis, steroid injections to the wrist may help alleviate pain. If x-ray results show arthritis due to an old break, the treatment plan will first focus on treating the arthritis through anti-inflammatory medications and wearing a splint when an individual feels pain in the wrist. Symptoms may include aching in the wrist, decreased range of motion of the wrist, and pain during activities such as lifting or gripping. If not treated correctly non-union of the scaphoid fracture can lead to wrist osteoarthritis.
This blood supply is tenuous, increasing the risk of nonunion, particularly with fractures at the wrist and proximal end. Arterial flow to the scaphoid enters via the distal pole and travels to the proximal pole.

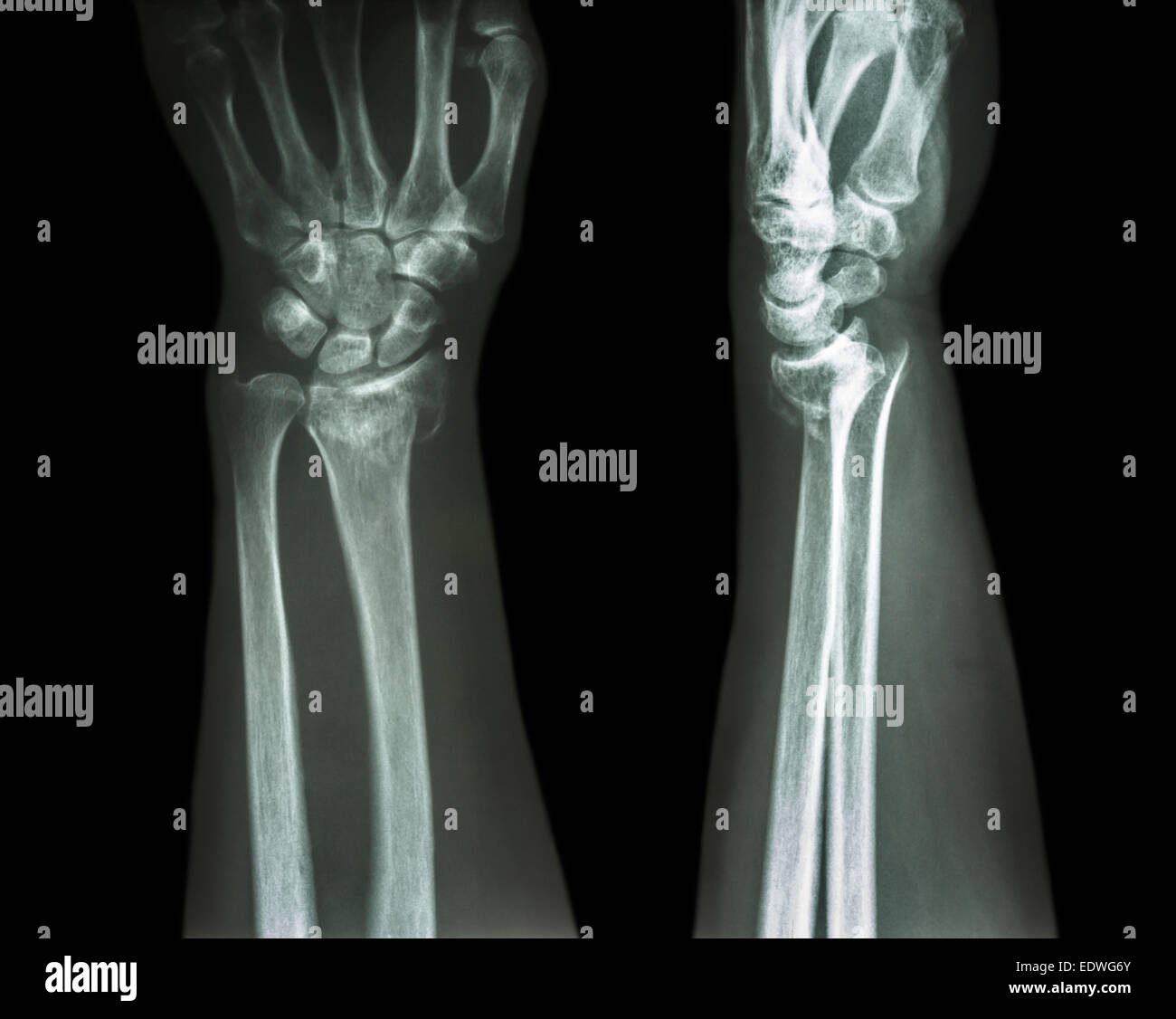
Non union can also occur from undiagnosed or undertreated scaphoid fractures. Fractures in the distal third are rarely complicated by AVN.Waist fractures in the middle third is the most frequent fracture site and has moderate risk of AVN.Fractures in the proximal third have a high incidence of AVN (~30%).Risk of AVN depends on the location of the fracture. from distal to proximal pole), the part proximal to the fracture is usually affected. Since the scaphoid receives its arterial supply in a retrograde fashion (i.e. 70-80% comes from (b.) the dorsal branch of the radial artery and travels towards the proximal pole.Īvascular necrosis (AVN) is one complication of scaphoid fracture. 20-30% of the blood supply (a.) comes from the volar branch of the radial artery and enters the bone at the tubercle. Vascular supply of the scaphoid comes from two different vascular pedicles. Complications Scaphoid pseudarthrosis, before and after treatment with Herbert screw. People with scaphoid fractures generally have snuffbox tenderness.įocal tenderness is usually present in one of three places: 1) volar prominence at the distal wrist for distal pole fractures 2) anatomic snuff box for waist or midbody fractures 3) distal to Lister's tubercle for proximal pole fractures. Males are affected more often than females. It is the most commonly fractured carpal bone. If the fracture is displaced then surgery is generally recommended. In those in whom the fracture remains well aligned a cast is generally sufficient. The fracture may be preventable by using wrist guards during certain activities. In such cases the affected area may be immobilised in a splint or cast and reviewed with repeat X-rays in two weeks, or alternatively an MRI or bone scan may be performed. Some fractures may not be visible on plain X-rays. Diagnosis is generally based on a combination of clinical examination and medical imaging. Scaphoid fractures are most commonly caused by a fall on an outstretched hand. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis of the proximal part of the bone, and arthritis. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. Nonunion, avascular necrosis, arthritis ĭistal radius fracture, De Quervain's tenosynovitis, scapholunate dissociation, wrist sprain Ī scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Carpal scaphoid fracture, carpal navicular fracture Īn X-ray showing a fracture through the waist of the scaphoid


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
